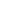
Amphioxus Branchiostoma lanceolatum

Lancelets (amphioxi) are cephalochordates, which belong to the superphylum Deuterostomia and are a basal clade of the phylum Chordata.
EMBRC expertise
Access
- Held in aquariums;
- Spawning can be induced in the aquarium and embryos can be collected daily during the four-month reproduction season;
- Adults can be shipped, except during the spawning season (May-July)
Lifespan of up to 7-8 years;
Practically the entire life cycle can be carried out in the aquarium: cultivation from the embryo stage to the adult stage.
Analysis tools
- Embryos are transparent and are thus suitable for cell imaging techniques, in situ in toto hybridisation, and immunohistochemistry;
- Functional gene analysis is possible; eggs can be micro-injected with mRNA or plasmids;
- Embryos can be used for functional approaches involving pharmacological treatments with molecules that can modulate signalling pathways (only low quantities required).
Scientific advantages of this model organism
- Amphioxi are cephalochordates, one of the three subphyla of the phylum Chordata. The anatomy of adult amphioxi is similar to that of vertebrates but simpler with a dorsal neural tube, a notochord, a ventral gut, segmented axial muscles, a perforated pharynx with gill slits (pharyngeal slits).
- Amphioxi are a choice experimental model for developmental biology and more especially in evolutionary developmental biology because it can help shed light on the evolutionary mechanisms at work in the invertebrate-vertebrate transition.
- Their genome is simple because cephalochordates diverged before the two genome duplication events that occurred before the diversification of vertebrates. This simplicity facilitates functional gene analyses because there is virtually no redundancy.
- Only three cephalochordate genera have been described: Branchiostoma, Epigonichthys and Asymmetron, representing 35 species. Branchiostoma lanceolatum is the Mediterranean species.
Available genetic resources
No mutant lines.
Databases
Genomic data on B. floridae and B. belcheri and transcriptomic data on B. floridae and B. lanceolatum.
Potential applications
Toxicological risk assessment
Emerging model for regeneration studie